Causes:
-Pancreatitis.
-Cholecystitis.
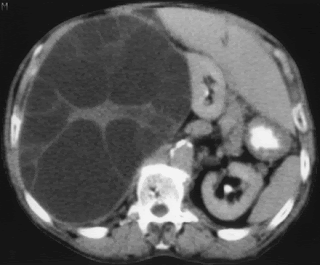
-Appendicitis:
Radiological appearances:Enlarged obstructed appendix containing fluid and appendicolith.
Normal appendix should contains air inside its lumen, if air is replaced with fluid, this is an accurate sign for appendicitis.
Appendiceal perforation do not cause pneumoperitoneum because before its perforation it should be obstructed leading to no leak of air inside peritoneal cavity.
-Diverticulitis:
First of all, to diagnose diverticulitis, you should see diverticulae.Then secondly, you should search for centipede sign(dirty surrounding fat planes).
If perforation occurs you can find pericolic abscess formation or fistulous tract with other intestinal loop or with the urinary bladder giving rise to air fluid level in the urinary bladder.
-Epiploic appendigitis:
If you take a look for the above images, you will find an oval lesion with central hyperdense are represents the thrombosed vessel, surrounded by a fatty zone. This is the picture in the acute stage, while in chronic stage, it will shows calcification.
-Hydatid disease:
Has the same criteria seen in hydatid disease of liver or elsewhere in body.




No comments:
Post a Comment